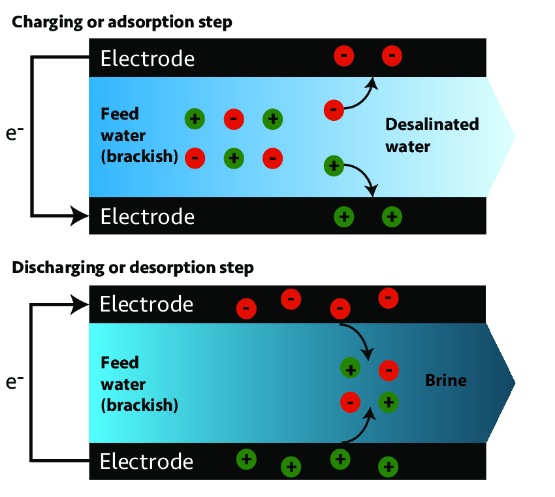
Capacitive Deionization (CDI)
Capacitive deionization (CDI): A difference in electrical potential between two electrodes is used in the deionization process known as capacitive deionization (CDI). The electrodes can contain intercalation host compounds or be entirely made of porous carbon particles, for instance. The cathode, or negatively polarized electrode, is used to store cations (positively charged ions), while the anions (negatively charged ions) are taken out of the water and stored in the positively polarized electrode.